|
Home
Boris
Sidis Archives
Most of the following
photos and descriptions were found at the online
Aesthesiometer "Measures the
distance required for two impressions on the skin to be distinguished from
each other, thereby measuring tactile sensitivity."
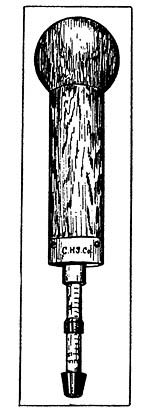
Algometer "Device for measuring
pain caused by pressure."
Automatograph "... a plate which lies on metal balls and thus follows every impulse of the hand which lies flat on it; the plate has an attachment by which the slightest movements are registered on a slowly moving surface. If the arm is held in a loop which hangs from the ceiling, the hand will still more easily follow the weakest impulse without our knowledge." more Foundations of Normal & Abnormal Psychology
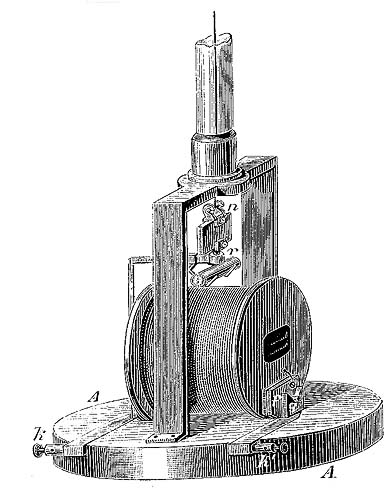
D'Arsonoval Galvanometer "A parallel beam of light from a small lamp reflects from the mirror attached to the top of the coil, and reflects back onto an external scale." more
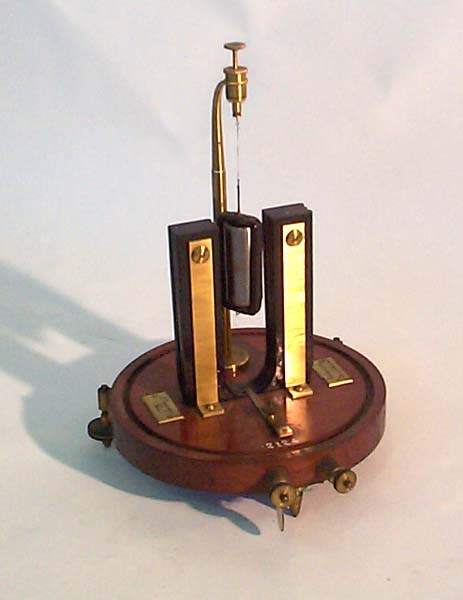
Deprez-d'Arsonval Galvanometer "The galvanometer proposed by Deprez and d'Arsonval is also defined as a mobile bobbin galvanometer and differs from those with a mobile magnet in that it is based on the interaction between a fixed magnet and a mobile circuit followed by the current being measured. Among the advantages of this type of galvanometer is a higher sensitivity based on the strong magnetic field inside the bobbin. From this galvanometer are derived all mobile bobbin instruments, both portable and non-portable." Nature and Causation of the Galvanic Phenomenon
Meissner and Meyerstein Mirror Galvanometer
Suspended Coil D'Arsonval Galvanometer "The coil is suspended from the top of the box by a thin phosphor-bronze strip, with the lower suspension being a loose coil of the same material." Nature and Causation of the Galvanic Phenomenon
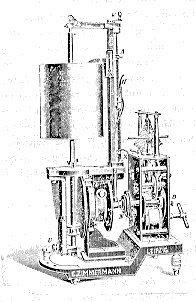
Ergograph "A device for measuring the work capacity of a muscle or group of muscles during contraction." The Causation and Treatment of Psychopathic Diseases Ergograph Writer "This illustration, unfortunately, does not show the critical connections, on the left, to the finger held in place by No. 388, and to the right, over the pulley, down to the weight that is repeatedly lifted by finger movement. The device, mainly, consists of a bristle holder which can write on a kymograph drum. This device is described as having an advantage over No. 391 (not illustrated), in that it has a cord which runs on two pulleys, which permits the writing apparatus to move in one direction to permit multiple recordings on the same kymograph drum. The band which moves in one direction is used to provide accumlulating measure of effort." Nature and Causation of the Galvanic Phenomenon
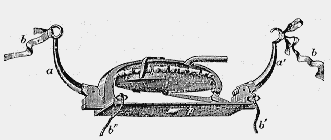
Esmarch Bandage
Hand Dynamometer "Person squeezes and hand strength is measured."
Inductorium "This apparatus, capable of producing induced currents at high potentials, consists of a primary coil of wire around a soft iron core." "In most cases, darkness, quietness, repose, the monotonous buzzing of an inductorium are conditions favorable to the hypnoidal state." The Value of the Method of Hypnoidization The Causation and Treatment of Psychopathic Diseases
Kymograph "An instrument for recording variations in pressure, as of the blood, or in tension, as of a muscle, by means of a pen or stylus that marks a rotating drum." Nature and Causation of the Galvanic Phenomenon
Kymograph Tambour "This is a drum with a nipple for a rubber tube which attaches to a kymograph. As the drum moves up and down in response to the air pressure, the writing bristle on the kymograph drum is moved." Nature and Causation of the Galvanic Phenomenon
Metronome "One common type of metronome is the wind-up metronome, which uses a weight on the end of a rod to control the tempo (slide the weight up the rod to decrease tempo, or down the rod to increase tempo). The pendulum rod swings back and forth in tempo; mechanics inside the metronome produce a clicking sound on each swing of the rod." "The patient is put in a relaxed, recumbent position; he is asked to put himself into as comfortable a position as possible, close his eyes, and attend to some monotonous stimulus such as the regular beats of a metronome." The Psychotherapeutic Value of the Hypnoidal State
Nernst Lamp "Nernst lamps were an early form of electrically-powered incandescent lamps. Nernst lamps didn't use a glowing tungsten filament, however. Instead, they used a ceramic rod that was heated to incandescence. Because the rod (unlike tungsten wire) would not further oxidize when exposed to air, there was no need to enclose it within a vacuum or noble gas environment; the burners in Nernst lamps could operate exposed to the air and were only enclosed in glass to aid in diffusing the light that was produced." moreNature and Causation of the Galvanic Phenomenon
Planchette "The board is supported by two castors and a pencil. When a person's fingers rest lightly on the board, it is supposed to trace words or drawings without conscious direction from that person. Spiritualists have used such devices to receive messages from the dead. "Unscrew the knurled knob, insert the pencil through knob, adjust the pencil to an equal length to the legs of the instrument and screw down the cap. Place planchette on a large sheet of paper and rest your hands lightly on the instrument, remaining perfectly passive and leaving it free to write."
Plethysmograph "An instrument that measures variations in the size of an organ or body part on the basis of the amount of blood passing through or present in the part." moreFoundations of Normal & Abnormal Psychology
Pneumograph "A device for recording the rate and extent of respiratory movements by means of a double-headed tambour stretched across the individual's chest, with an attached rubber tube for communicating the movements to a recording tambour."
Marey Pneumograph "Device for indicating movements of the breast due to breathing. It is mounted on a spring plate which, when the breath is expired, returns to its original position."
Rheotome "A vibrating metal reed in a circuit with an electromagnet and a telegraph key." "With his eyes closed he is directed to listen to the monotonous vibration of the ribbon rheotome..." The Value of the Method of Hypnoidization The Causation and Treatment of Psychopathic Diseases
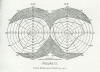
Skeel's Self-Recording Perimeter "In taking fields, it is my habit to make a pencil mark on each meridian as the limit of vision on that meridian is determined, and then outline the whole field when I have finished."
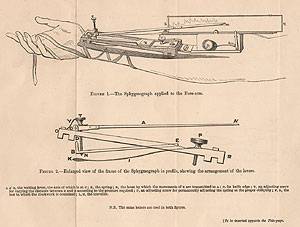
Sphygmograph "The sphygmograph allowed physicians to measure the pulse, and most importantly, to record it. Previously the pulse was measured by placing fingers on the wrist of the patient and applying pressure. The sphygmograph was a first step in standardizing the recording and evaluation of pulses using technology." Animation Foundations of Normal & Abnormal Psychology
|